Container Segment
in € million |
2017 |
2016 |
Change |
|||
Revenue |
746.6 |
694.6 |
7.5 % |
|||
EBITDA |
194.7 |
201.5 |
- 3.3 % |
|||
EBITDA margin in % |
26.1 |
29.0 |
- 2.9 pp |
|||
EBIT |
109.4 |
117.8 |
- 7.2 % |
|||
EBIT margin in % |
14.7 |
17.0 |
- 2.3 pp |
|||
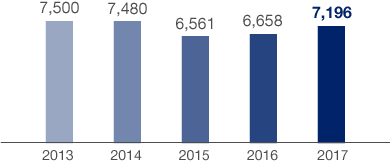
Container throughput in thousand TEU |
7,196 |
6,658 |
8.1 % |
HHLA’s container terminals handled 7,196 thousand TEU in the 2017 financial year, 8.1 % more than in the previous year (6,658 thousand TEU). The volume development in the reporting period was largely dominated by the realignment of shipping consortia and the resulting change in liner service structures. This positive development was facilitated by intensive sales activities and the provision of handling services in line with customer needs, especially with regard to ship sizes.
Development in Container Throughput
in thousand TEU
Container throughput at the three container terminals in Hamburg increased strongly by 8.3 % to 6,904 thousand TEU (previous year: 6,375 thousand TEU). This was mainly due to a 14.9 % year-on-year rise in Asia traffic (Far East–Northern Europe) and significant growth in feeder traffic in the Baltic region, especially to Sweden and Poland. By contrast, traffic to and from Russia was still affected by the EU’s ongoing economic sanctions and only reached the prior-year level over the full twelve months, despite initial gains in the first half of 2017. The proportion of seaborne handling accounted for by feeders edged up to 24.5 % in 2017 (previous year: 24.0 %).
At the HHLA Container Terminal Odessa (CTO), container throughput rose slightly by 3.4 % to 292 thousand TEU (previous year: 283 thousand TEU). Due to overcapacities on the market, competition intensified further in 2017. Despite the slower volume trend, however, CTO continues to hold a dominant regional market position among the Ukrainian ports.
Revenue increased by 7.5 % year-on-year to € 746.6 million (previous year: € 694.6 million) and thus lagged somewhat behind the rise in seaborne volumes. Average revenue was affected by the slightly higher proportion of lower-margin feeder traffic, adjustments to individual handling rates due to the realignment of shipping consortia, and the temporary rise in storage charges. The average revenue per container handled at the quayside dipped by 0.6 % year-on-year in the 2017 financial year.
Changes in the segment’s EBIT costs in the 2017 financial year stemmed largely from the increase in handling services and additional expenses. Total one-off expenses of approximately € 25 million related to measures for the organisational restructuring and harmonisation of existing pension schemes, which put further pressure on the cost structure in the 2017 financial year. The year-on-year increase in material costs was largely due to volume and price trends. IT costs increased due to the implementation of a new terminal operating system. All in all, EBIT costs were up by 10.5 %. Adjusted for the additional expenses, however, the increase was just 6.1 %. It should be noted that the anticipated utilisation-related economies of scale have not yet achieved their full impact on costs. The operating result (EBIT) amounted to € 109.4 million (previous year: € 117.8 million). The EBIT margin reached 14.7 % (previous year: 17.0 %). Adjusted by additional expenses, the operating result increased by 14.1 % year-on-year.
As shipping companies are still taking delivery of container mega-ships for the Far East–Europe trades, there is likely to be a further rise in the number of vessels of this size calling directly in Hamburg. With this in mind, the company continued to expand its facilities to cater for larger ships. Four additional automated storage blocks have been put into operation at the Container Terminal Burchardkai (CTB) and a further three container gantry cranes have been installed at the berth of the Container Terminal Tollerort (CTT).
In maritime logistics, a terminal is a facility where freight transported by various modes of transport is handled.
A TEU is a 20-foot standard container, used as a unit for measuring container volumes. A 20-foot standard container is 6.06 metres long, 2.44 metres wide and 2.59 metres high.
A TEU is a 20-foot standard container, used as a unit for measuring container volumes. A 20-foot standard container is 6.06 metres long, 2.44 metres wide and 2.59 metres high.
Vessels which carry smaller numbers of containers to ports. From Hamburg, feeders are primarily used to transport boxes to the Baltic region.
Revenue from sales or lettings and from services rendered, less sales deductions and VAT.
Earnings before interest and taxes.
In maritime logistics, a terminal is a facility where freight transported by various modes of transport is handled.
A rule of economics which says that higher production quantities go hand in hand with lower unit costs.
Earnings before interest and taxes.
A crane system used to load and discharge container ships. As ships are becoming larger and larger, the latest container gantry cranes have much higher, longer jibs to match.